摘要
基于3.0版本EventBus分析。
1.1 创建EventBus
我们一般通过EventBus.getDefault()获取到EventBus对象,这里使用单例模式,保证getDefault()得到的都是同一个实例,如果不存在实例,就调用EventBus的构造方法。
|
|
通过初始化EventBusBuilder()对象来初始化EventBus的一些配置,将配置解耦,使代码结构更清晰。
1.2 注册过程源码简析
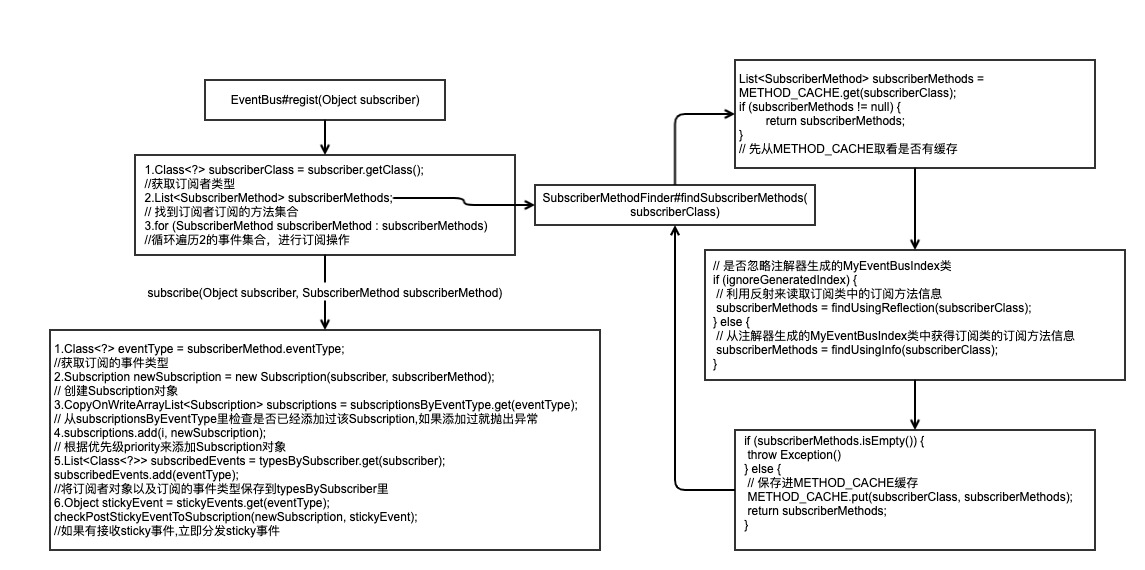
SubscriberMethodFinder的实现
在3.0版本,
EventBus提供EventBusAnnotationProcessor注解处理器在编译期通过读取@Subscribe()注解并解析,处理其中所包含的信息,然后生成java类来保存所有订阅者关于订阅的信息,这样就比在运行时使用反射来获得这些订阅者的信息速度要快。我们可以参考
EventBus项目里的EventBusPerformance这个例子,编译后我们可以在build文件夹里找到这个类MyEventBusIndex类(当然类名是可以自定义的),我们大致看一下生成的MyEventBusIndex类是什么样的:12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546public class MyEventBusIndex implements SubscriberInfoIndex {private static final Map<Class<?>, SubscriberInfo> SUBSCRIBER_INDEX;static {SUBSCRIBER_INDEX = new HashMap<Class<?>, SubscriberInfo>();putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(org.greenrobot.eventbusperf.testsubject.PerfTestEventBus.SubscriberClassEventBusAsync.class,true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {new SubscriberMethodInfo("onEventAsync", TestEvent.class, ThreadMode.ASYNC),}));putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(org.greenrobot.eventbusperf.testsubject.PerfTestEventBus.SubscribeClassEventBusMain.class,true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {new SubscriberMethodInfo("onEventMainThread", TestEvent.class, ThreadMode.MAIN),}));putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(org.greenrobot.eventbusperf.testsubject.SubscribeClassEventBusDefault.class,true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {new SubscriberMethodInfo("onEvent", TestEvent.class),}));putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(org.greenrobot.eventbusperf.testsubject.PerfTestEventBus.SubscribeClassEventBusBackground.class,true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {new SubscriberMethodInfo("onEventBackgroundThread", TestEvent.class, ThreadMode.BACKGROUND),}));putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(TestRunnerActivity.class, true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {new SubscriberMethodInfo("onEventMainThread", TestFinishedEvent.class, ThreadMode.MAIN),}));}private static void putIndex(SubscriberInfo info) {SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.put(info.getSubscriberClass(), info);}@Overridepublic SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {SubscriberInfo info = SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.get(subscriberClass);if (info != null) {return info;} else {return null;}}}
可以看到是使用一个静态的HashMap即SUBSCRIBER_INDEX来保存订阅类的消息;其中包含订阅类的class类型、是否需要检查父类、以及订阅方法信息的SubscriberMethodInfo数组;SubscriberMethodInfo中保存了订阅方法的方法名、订阅的事件类型、触发线程、是否接收sticky事件、以及优先级priority。
我们可以通过EventBus.builder().addIndex(new MyEventBusIndex()).build()将MyEventBusIndex配置进EventBus,这样就能在SubscriberMethodFinder类中直接查找出订阅类的信息,不需要再利用注解判断了,当然这种方法是作为EventBus的可选配置。
SubscriberMethodFinder同样提供了通过反射来获得订阅类信息的方法,即通过findUsingReflection方法:12345678910111213private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingReflection(Class<?> subscriberClass) {// FindState 用来做订阅方法的校验和保存FindState findState = prepareFindState();findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);while (findState.clazz != null) {// 通过反射来获得订阅方法信息findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);// 查找父类的订阅方法findState.moveToSuperclass();}// 获取findState中的SubscriberMethod(也就是订阅方法List)并返回return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);}
通过FindState类来做订阅方法的校验和保存,并通过FIND_STATE_POOL静态数组来保存FindState对象,可以使FindState复用,避免重复创建过多的对象。
通过findUsingReflectionInSingleClass()来具体获取订阅的方法:
- 最后再通过
getMethodsAndRelease()返回List<SubscriberMethod>。
1.3 解除注册源码简析
解除注册只要调用unregister()方法即可,分别从typesBySubscriber和subscriptionsByEventType移除订阅者相关信息。
1.4 事件分发过程源码简析
|
|
1.5 事件分发线程处理过程源码简析
1.5.1 mainThreadPoster
|
|
1.5.2 backgroundPoster
|
|
1.5.3 asyncPoster
|
|
默认eventBus.getExecutorService()的配置是Executors.newCachedThreadPool()使用无界队列SynchronousQueue当事件过多时,会出现OOM。